ECG waveforms using different driven right leg circuits in the noisy... Download Scientific

An Electrocardiogram or ECG Amplifier with Right Leg Drive is explained in this video which is the 209th example in my Analog Circuit Playlist. The first st.
Solved The right leg driven circuit for the ECG signal
IMEC. Leuven, Belgium Aakash.Patel@imec.be. Abstract—A digital system for capacitive ECG measurement is proposed, including a digital driven right leg loop, which compared to current analog systems, can provide significantly greater robustness for the placement of electrodes in real-world scenarios such as inside a vehicle, as well as greater.
Figure 2 from Can drivenrightleg circuits increase interference in ECG amplifiers? Semantic

To maximize your common mode rejection ratio, you may want to consider implementing active grounding or a driven right leg in your ECG (EKG) design! Active g.
Artikel3
I am currently writing my Bachelor Project about an ECG amplifier. Common mode voltage on the body has a much higher amplitude than an ECG signal. To attenuate common mode noise a differential amplifier is used. Furthermore, a circuit known as "Driven Right Leg circuit" is used further to attenuate common mode noise.
(PDF) An ECG measurement IC using drivenrightleg circuit Alex Wong Academia.edu

The total capacitor usage is 1nF, less than the specified maximum capacitor usage. To sum up, the ECG sensor is designed using the "right leg drive circuit" and a new type of amplifier is designed to eliminate common-mode interference and improve the performance of the amplifier. Export citation and abstract BibTeX RIS.
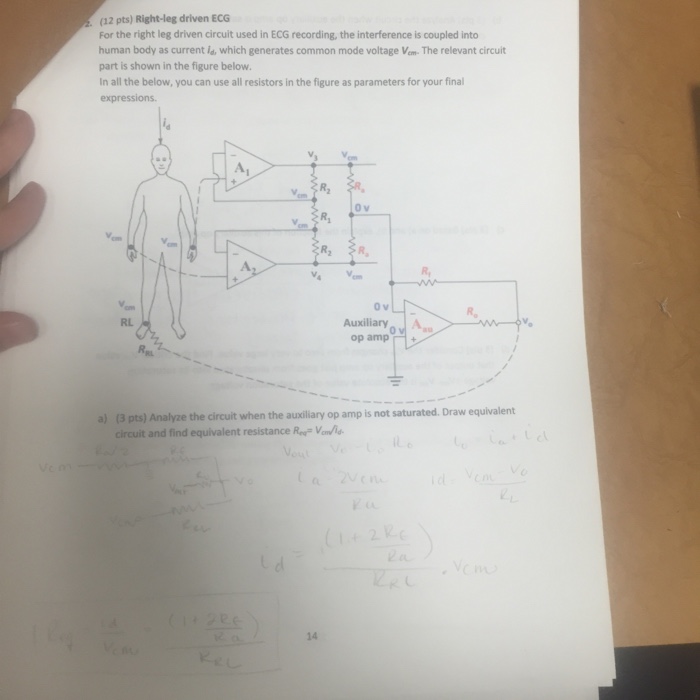
Solved (12 pts) Rightleg driven ECG For the right leg
The Driven-Right-Leg (DRL) circuit has been used for about 50 years to reduce interference due to common-mode voltage in biopotential amplifiers in scenarios that range from fixed equipment.
ECG Electrode Placement GetBodySmart

In this paper, an electrocardiographic (ECG) signal processing IC, which is used for portable biomedical application, was designed using continuous-time technique. The circuit consists of an instrumentation amplifier (INA) with driven-right-leg circuit (DRL), a 5th order G/sub m/-C low pass filter (G/sub m/-C LPF) operating in sub-threshold mode, and amplifiers. DRL circuit is used to detect.
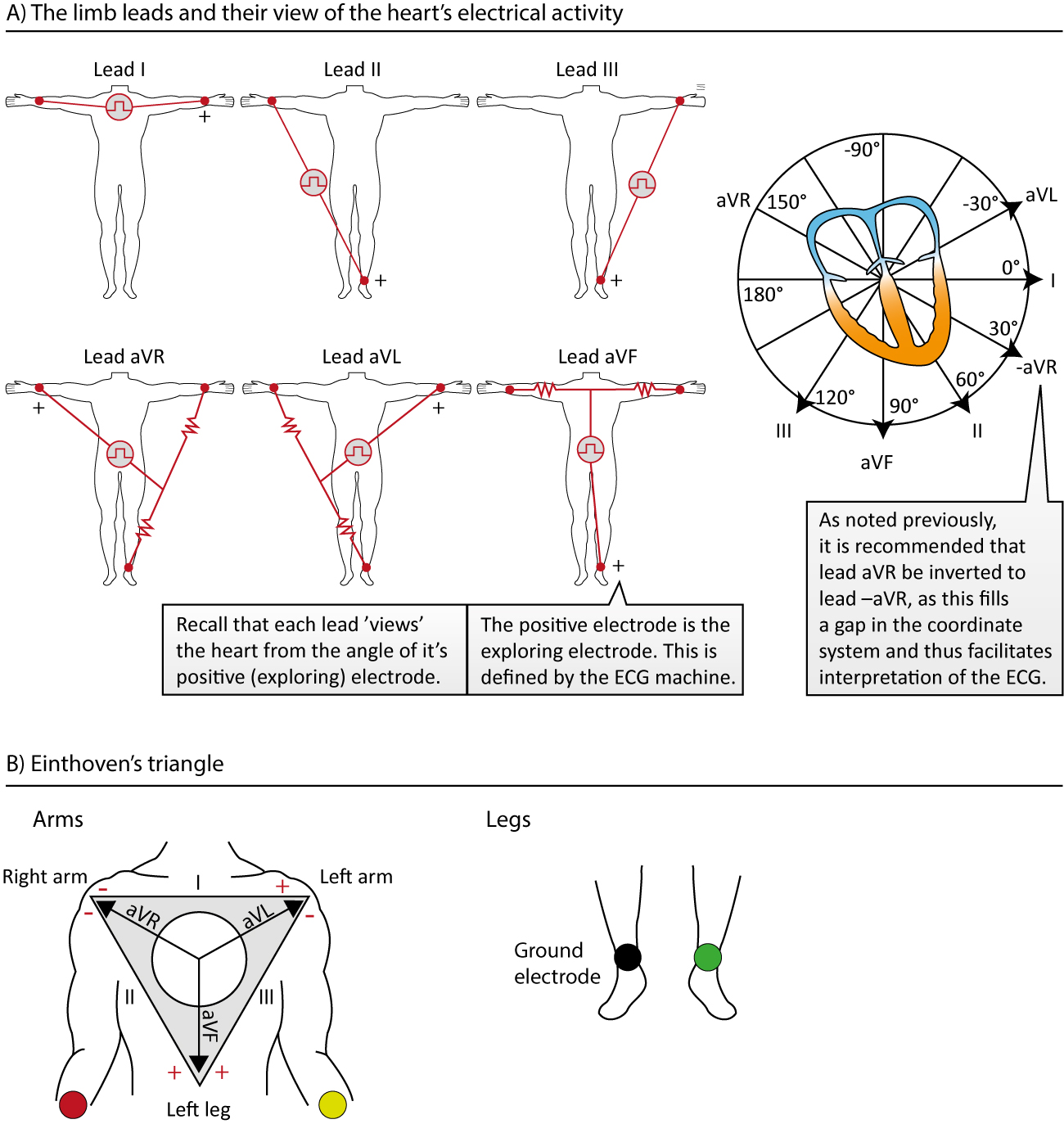
The ECG leads electrodes, limb leads, chest (precordial) leads, 12Lead ECG (EKG) ECG learning
The Driven-Right-Leg (DRL) circuit has been used for about 50 years to reduce interference due to common-mode voltage in biopotential amplifiers in scenarios that range from fixed equipment supplied from power lines to battery-supplied ambulatory monitors, and for systems that use gelled, dry, textile, and capacitive electrodes. However, power-line interference models predict that for.
ltspice Stability of driven right leg circuit in ECG amplifier Electrical Engineering Stack

The right-leg-drive circuit is used in the overall process to ensure good common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) performance. For the newly designed op-amp, its gain can reach 60db, and the operating.
Development and test of a portable ecg device with dry capacitive electrodes and driven right
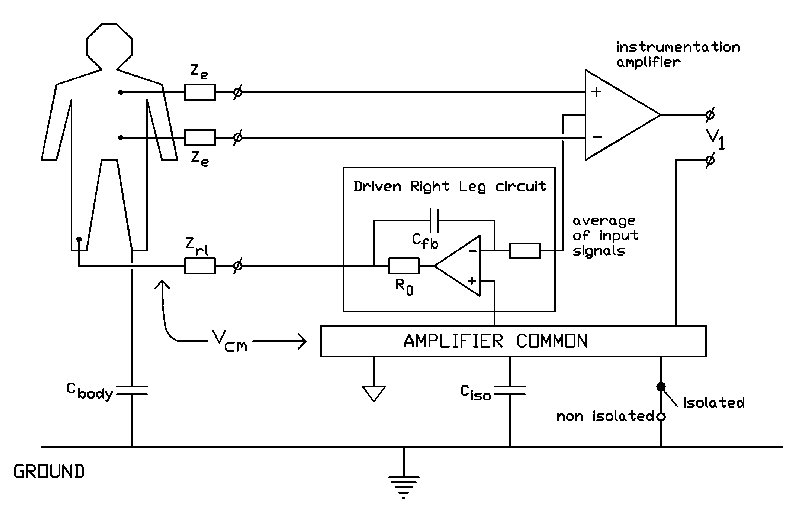
6. A driven right leg (DRL) circuit is often added to a biopotential amplifier to reduce the common mode voltage (i.e. to increase the common mode rejection ratio, CMRR). A basic form of biopotential amplifier is just an instrumentation amplifier which has two stages: a buffer stage and a single output amplification stage.
12Lead ECG Placement Guide with Illustrations
A new operational amplifier (op-amp) design is proposed in this study, and it is integrated into the traditional "right-leg-drive" circuit to cancel out the common-mode interference and improve the performance of the amplifier. The low-power consumption and low-noise sensor remain an important challenge in Electrocardiogram (ECG) sensor field. A new operational amplifier (op-amp) design is.
Figure 5 from An ECG measurement IC using drivenrightleg circuit Semantic Scholar

Improving CMR Using the RLD Amplifier with the ADS1298. Consider a situation when the right arm (RA) electrode is open and the left arm (LA) electrode is snug. In this case, the output common-mode of the PGA is driven away from the reference voltage, which causes the RLD feedback loop to fail.
Driven right leg circuit Semantic Scholar
The driven-right-leg circuit is often used with biopotential differential amplifiers to reduce common mode voltage. We analyze this circuit and show that high loop gains can cause instability. We present equations that can be used to design circuits that minimize common mode voltage without instability. We also show that it is important to consider the reduction of high-frequency interference.
AMPLIFIER IN ECG RECORDING, DIFFERENTIAL & INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER, RIGHT LEG DRIVEN AMPLIFIER

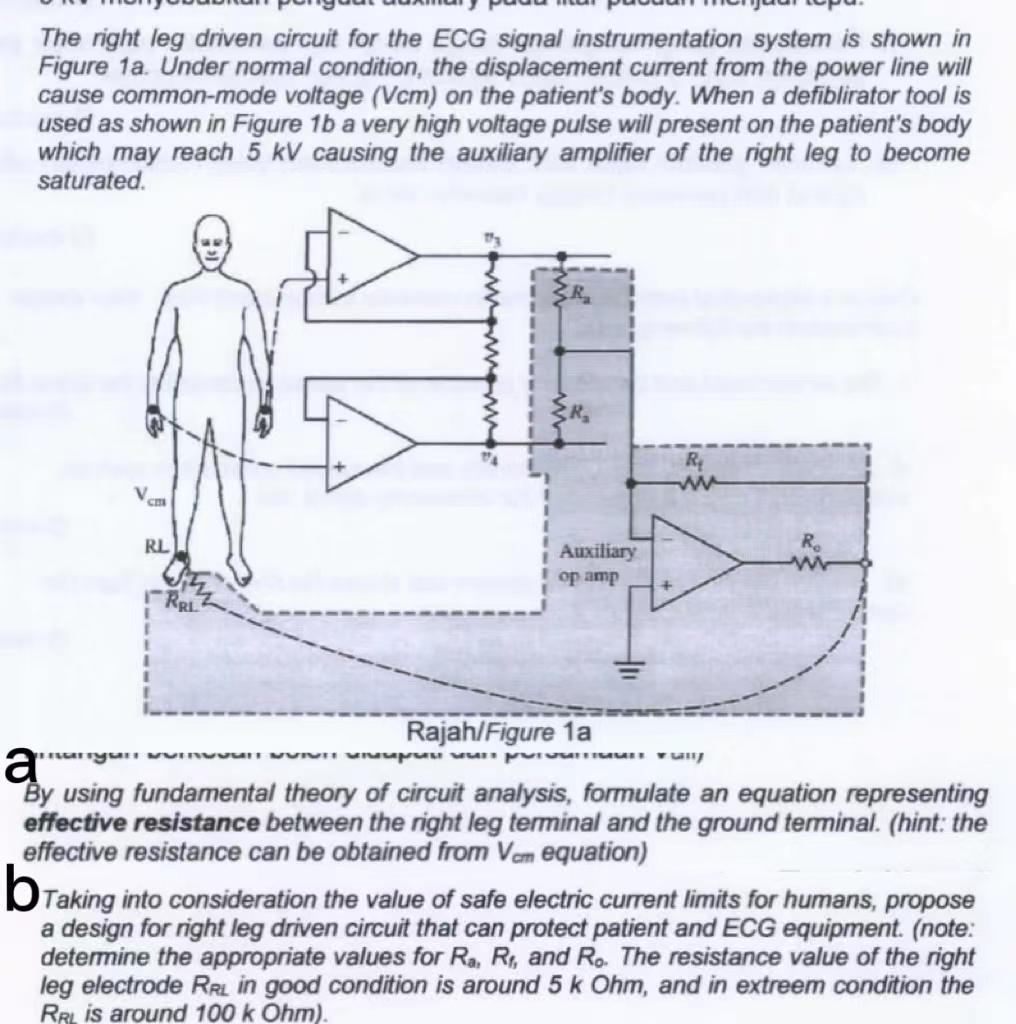
Modification to conventional ECG system Driven right−leg circuitry In modern ECG recording systems, the patient is often not grounded. Instead, the right leg electrode is connected as shown in Figure 14 to the output of an auxiliary op−amp. The common−mode voltage on the body is sensed by two averaging resistors Ra, inverted and fed
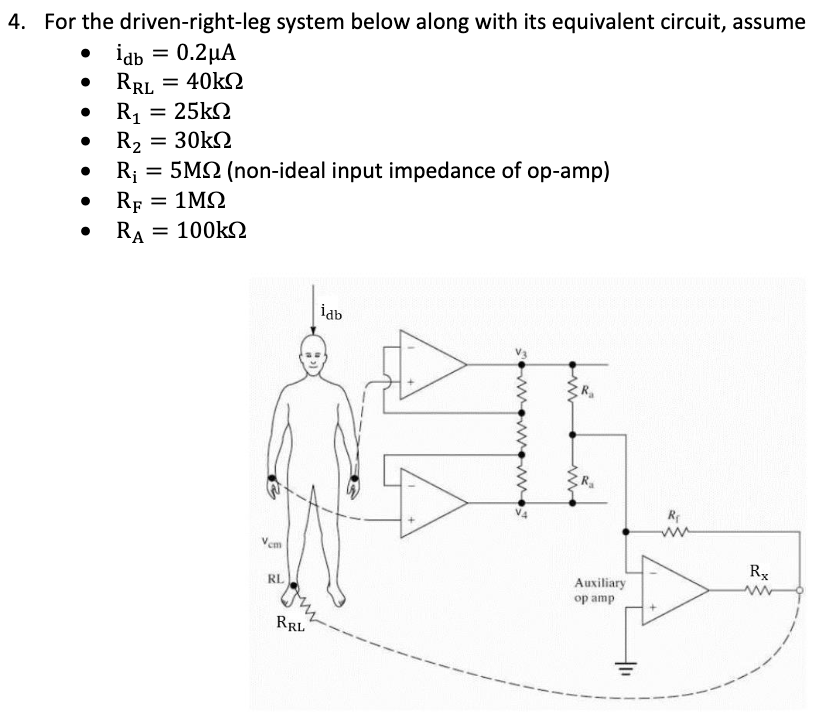
Solved For the drivenrightleg system below along with its
two electrodes are riding on top of. This voltage is mirrored around the. reference voltage (usually half the supply) and driven back to the body. In summary, as the body is capacitively pulled away from the reference voltage, the RLD amplifier pulls it back in. It is traditionally named Right Leg Drive. because the driving is done in the part.
Figure 2 from A Driving Right Leg Circuit (DgRL) for Improved Common Mode Rejection in Bio

The feedback circuit is named DRL as it works based on the same principles as the popular driven right leg (DRL) feedback loop used in ECG recording [19]. The feedback loop improves CMRR by 20×.